Learning Note: The Relationships between Operating System and Programs
This article is a summary of Chapter 9 of:
Yazawa, H. (2015). 程序是怎么跑起来的[How Program Works] (L. Fengjun, Trans.). People's Posts and Telecommunications Press
A Brief History of Operating Systems
The predecessor of operating systems are monitoring programs that can automate the loading and running of programs. These monitoring programs are used to load programs into the memory.
Later, it is found that many common functions, like type texts with keyboards, or printing texts on the monitor, are the same among different programs. These basic I/O features are added to the monitoring programs, forming the early version of operating systems.
Today's operating systems integrate additional utilities like hardware control programs, programming language compilers and interpreters, and text editor. For short, a operating system is not a single program, but a combination of many programs.
Operation Systems as a Layer between Programs and Hardware
Programs running in the operating system normally do not control computer hardware directly, but control hardware through invoking commands provided by the operating system, and the operating system will execute the commands on hardware level. For example, when called function time() in C, the function invokes commands in the operating system used to control the real-time clock IC.
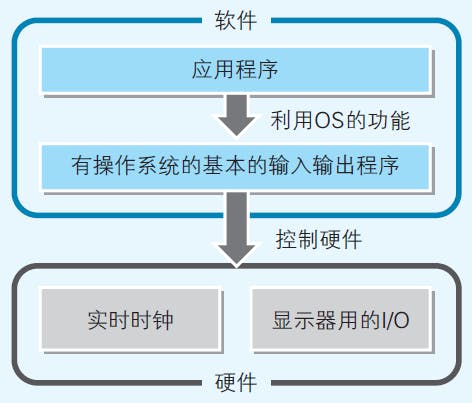
Fig 1. Operating System is the Layer between Hardware and Programs. Image reproduced from (Yazama, 2015)
The API operating systems provide for hardware control are called system call. Functions like time() in programming languages use of system calls in their internal implementation. Since we expect programming languages to run on different operating systems, the specific system calls in different operating systems are embedded in the internal implementation of programming languages. As a result, functions like time() are able to work on different operating systems.
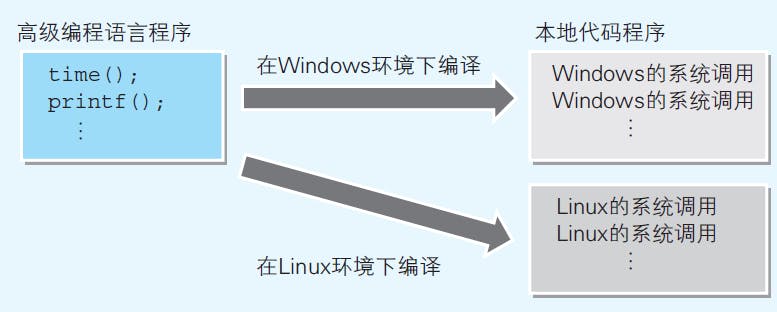
Fig 2. Programming Languages unify System Calls in their API. Image reproduced from (Yazama, 2015)
To give another example demonstrating the abstrations provided by operating systems and programming languages, consider the functions used to read and write files in C: fopen(), fputs(), fclose(). File is an abstration on hard disk sectors. The whole process of finding a cvalid hard disk sector to store data, writing data to hard disk is simplified to the reading and writing of files for programmers.
Features of Windows Operating System
1 32/64 bit system:
The number of bits in an operating system represents the size of data that is most efficiently processed by the system. For example, it is more efficient for a 32-bit Windows sytem to process a 32-bit int type than a 16-bit MS-DOS sytem, since for the latter one it takes two operations instead of one.
2 Provide API Functions for System Call:
Windows provide system calls in the form of API functions. These API are stored in DLL files and are normally written in C. The Win32 API for 32-bit systems are stored in user32.dll
3 GUI (Graphical User Interface):
GUI refers to user interface with interactive windows and icons on the monitor. Though GUI makes the use of programs more convenient, it creates more workload for the programmers. In GUI, users may not be using the program in a given process, so the program must ensures correct running with any given order.
4 WYSIWYG:
WYSIWYG (What you see is what you get) refers that content displayed on the monitor can be directly printed sith printers.With this function, programmers do not need to implement seperate programs for display on monitor and printing with printer.
5 Multitasking:
Multitasking refers to the ability to run multiple programs simultaneously. Windows achieves this with clock segmentation, that is, switching the program running in short time intervals. Since the interval are too short to be perceptable, viewed from the users, it appears that mutiple prgrams are running together.
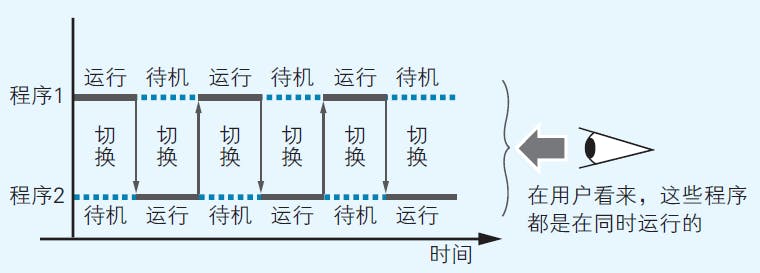
Fig 3. Multitasking with clock segmentation. Image reproduced from (Yazama, 2015)
6 Networking and Database Functionality:
In Windows, networking and database are added as standard functions. Technically, they are not part of the operating system, but are middleware, programs that work at the middle of operating system and applications. Operating system and middleware together are called system software.
7 Plug-and-Play:
Plug-and-Play refers a functionality that when a new device is connected to the computer, the operating system will automatically install its device driver. Device drivers are used to provide basic I/O operations for hardware. Drivers for most basic hardware device like keyboard, mouse, monitor, and hard disk are usually pre-installed in the operating system. Sometimes, DLL files are install along with device driver, and the DDL stores API for the hardware device. Windows allow flexible adding of both device drivers and their corresponfing APIs.